India population is roughly 1.27 billion or 127 Crore & more than two third of our population is below the age of 35 years, an age limit that is generally considered as boundary of youth. India has 830 million below the age of 35 years
Age Structure: (Demographic Profile, est. 2016)
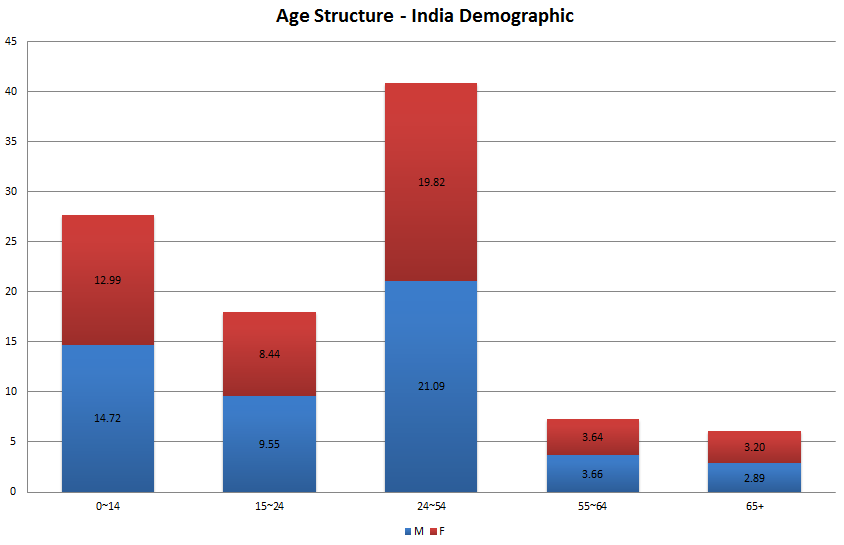
- Total Dependency Ratio: 52.5
- Youth Dependency Ratio: 43.9 (Dependent on Parents)
- Elderly Dependency Ratio: 8.6 (Dependent on Children)
India younger population is more than 100 million more than the total population of all the G7 countries combined. This dividend will continue for another 25-30 years. It is great opportunity to convert India into real Super Power. Although India currently has the largest set of young people, the issue is that a disturbingly large portion of this group is either totally unemployed or only partially employed and that also primarily in the unorganized sector. This is due to a variety of factors including skills shortage and lack of jobs. It is not hard to see the implications if this young population is not given jobs and thereby an opportunity for a respectable way of living. Apart from the lost opportunity in terms of GDP growth and rise in economic activity, this potentially entails social unrest that could have a negative knock on effect on India’s positive growth outlook.
Only 10% of Indian Workforce is working in organized sector; just 2.5% of working population has any vocational training, compare to average of 60-70% in developed countries. Out of 12 millions students graduating every year only 20% has the relevant skill set. The women comprise of 49% in Indian population but the women workforce is only 21% in organized & unorganized sectors. India’s higher education segment is the largest in the world & it ranks 2nd in terms of student enrollment in higher education. There are 799 Universities, 39,071 Colleges & 11923 Standalone Institutes for higher education with student enrollment of 34.2 millions.. In primary education we have 15 lakh plus schools with more than 260 Millions students enrolled in India.. In addition there are 459 General, 101 Technical, 64 Agriculture & Allied 50 medical, 20 law , 11 Sanskrit & 7 Language Universities. The figure are as of 2015 -16 & it is growing day by day… There are around 13000 plus ITI Industrial Training Institutes in India most of them are defunct. The courses/curriculum are irrelevant for the current time & needs to be changed. Time for Corporate to take over these ITI & run the program to suit the business requirements
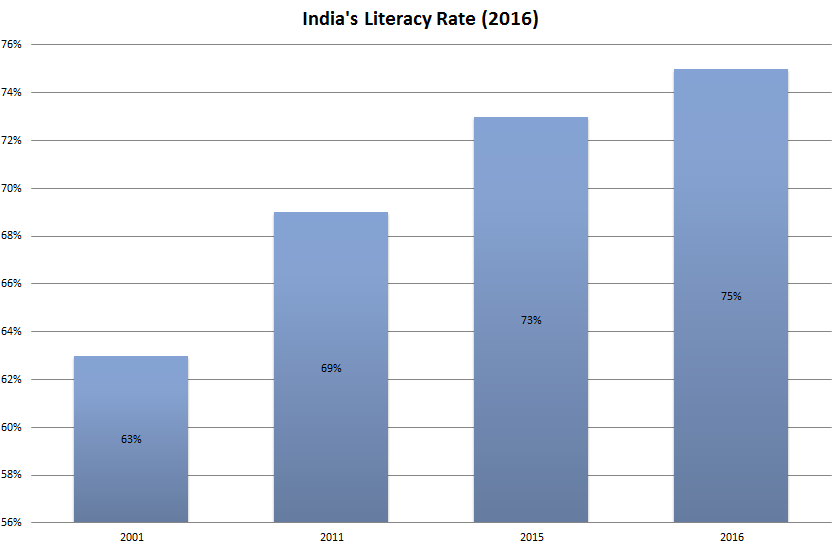
At Undergraduate level the highest number (40%) of students is enrolled in Arts/Humanities/Social Sciences courses followed by Science (16%), Engineering & Technology (15.6%) & Commerce (14.1%) & rest in other courses. Indian literacy rate is estimated to be at 75 per cent in 2016 as compared to 63 per cent in 2011. However, there is still a lot of potential for further development in the education system. Also, the questions have started getting raised on the quality of the education imparted by the Institutions
- Faculty to student ratio is 26:1 as compared to global average of 15:1
- Education Expenditure 3.8% of GDP is lower than the Health Expenditure which is 4.7% of GDP
The Priority Areas are Education, Skill Development and Employment, Entrepreneurship, Health, Sports, Promotion of Social values, Community Engagement, Youth Engagement & Inclusion, Social Justice
Quality of education both primary & secondary is woefully low in our country. A large part of population is unable to find appropriate avenue for education & employment. We also have a very poor level of vocational training /education. One needs to have a basic level of skilling to be able to add value to the workplace. A lot of companies are coming together to facilitate & support the skilling of potential workers but it’s a drop in an ocean. There is a need for strong partnership & regular dialogue between Corporate, Academia, Government & society at large.
Academia only defines one part of the job “What”. The other important part “ How to” is often left to experience. The difficult part is to sustain & progress in job once you get it. The subject like Working in Teams, Understanding the needs of others, Communicating effectively, Understanding Culture, Taking decision in ambiguous situations, Managing Emotions & Managing Relationship are not adequately touched which forms the core in Corporate Sectors to deliver performance.
India’s Demographic dividend may actually means that we are sitting at the tip of a volcano, ready to erupt at any given point of time. Today we are in jobless growth period, which we cannot continue to afford, for a long. We need to adapt an inclusive growth model to have success. Growth is the best skill development agent for a country like India. Automation (AI & Robotics) is at its peak & also taking away lot of jobs in Industry/Sectors. We need to adopt a Bottom up approach to the socio-economic aspects of the opportunity. There is a large onus as nation to ensure that under utilized potential across the country get tapped else we will not be in a position to en cash the demographic dividend. Current Government is focused on Nation Building, New BHARAT… Swach BHARAT & launched ambitious initiatives such as Make in India, Skilling India, Digital India, Startup India & Educate India.
We need to work on 90% of people who are engaged in informal employment to promote & encourage them to get into mainstream:
- Motivate: Youth be taught to stand up for their legitimate rights & encouraged to take more responsibility for their own & country growth
- Educate: We must prepare & produce efficient & employable youth to utilize their skills for the nation building
- Skill Building: There is need to interact with universities to devise Skill Development training program for students, so that required skills can be imparted at an early stage of career as oppose to running an expensive training program at customer expense
- Encourage Enterprises: Youth be encouraged to take up small enterprises & negligible sectors to compete among themselves & with big & small corporate houses
- Affordable Credit: The government /third party should ensure easy access to timely & adequate credit to people on reasonable terms & at the same time enforce strict end use & prompt repayment to banks
- Build Infrastructure: Build Power, Transport, Roads, Ports, Airport Terminals, Cold Storage’s, warehouse facilities to generate employment. Complete the existing projects & start the new ones
- Explore options for Public Private Partnership (PPP) & Build Own Operate Transfer (BOOT) or Design, Build, Finance Operate Transfer (DBFOT) Models in Healthcare, Infrastructure & Education
- Promote Schemes like MGNREGA & UDAAN with little fine tuning, Countrywide
- Upgrade Technology: Leverage Human Capital with use of Technology to create wealth. Use technology in Agriculture, Organic Farming to engage youth as it can become backbone for the country
Job Creating Sectors are:
- Construction & infrastructure Sector – Housing, Ports, Airports, Power, Roads, Cold Storage, Ware Houses facilities
- Agriculture Sector – Organic Farm, Fishery, Hatchery, Poultry
- Manufacturing Sector
- Retail Sector
- IT & ITES Sector
Need of the hour:
To create/convert School/Colleges/ITI/ Business Schools/ Engineering Colleges/Universities to National Assets and conduct SKILL DEVELOPMENT / UPGRADATION Programs round the year apart from running vocational colleges in these infrastructure. It will help to optimize the use of infrastructure apart from helping youth to gain Soft/Hard skills. Treat Academia professionals with respect, in terms of dignity & rewarding them suitably for their work… today Academia is preferred as last option. Upgrade course curriculum’s reforms to stay relevant.
Focus & develop Soft skills/Competencies: i.e. Energy & Impact, Effective Communication Skills, Build Relationship & Trust, Effective Team Player, Willingness to learn, Analytical Thinking & Reasoning Skills, Basic Understanding of Business, Keep organization before Self, Integrity, Humility & Respect, Achievement Drive, Ability to resolve Conflicts.
- Real time Experience/Success /Failure Stories Sharing
- Partnership & Collaboration between Government/ Academia/ Industry & Society
- Mentoring/Coaching/Incubation
- Faculty Development Programs
- Inviting FDI into Higher Education Systems
- E learning & on line tutoring / Video Content Developing & Delivery
- There are 6 basic categories of after-hour Institutional activities.
- Cultural and social (i.e. community theaters)
- Youth activities, including day care (i.e. athletic/Sports Education, associations)
- Resource use and information dissemination (i.e. community libraries)
- Health, leisure, and recreation (i.e. swimming and fitness clubs)
- Adult learning (i.e. remedial, retraining, informal, and advanced studies)
- R & D Initiative
In India, the demand for skilled manpower has grown exponentially, fueled largely by the boom in knowledge-based industries like the Technology sector. This increased demand for higher education is currently served largely by private colleges; with probably less than 10% are government sponsored. The basic model for most of the colleges in India is to be a teaching-only place, with no participation in any R&D activity thus creating a gap between what is required by the Industry and what is been taught in the Institutes. In today’s fast paced Global Economy, knowledge is dynamic and is rapidly changing. The relationship to practice is what gives true understanding of tools, techniques, and concepts that are taught in a course, as the basic goal of most of the courses is to help apply concepts to solve some problems. Without this understanding of relationship between the concepts being taught to practice, the material that will be taught will be highly conceptual and unsuitable for educating people. To understand this relationship to practice, either the teacher should be such that he knows the concepts and is also a practitioner, or should have much higher and deeper level of knowledge in the subject such that linkages are well understood.
To satisfy these requirements:
- Teacher is to be a researcher in the area in which he teaches, more so in case of technical education
- This will also helps in supporting the development of the teacher by way of giving him / her freedom to innovate and create
- Researcher gets the freedom to select the problems he works on, and through his research he creates new knowledge
- The student is been given an environment where he practices what he learns in the classroom thus giving more edge in understanding the real time problems in realistic scenarios
If the level of education of colleges is to be improved, an impetus must be given to get some degree of R&D going in colleges and universities. Improving syllabi, or doing short-term teachers training programs, will only have an effect for a short time. For maintaining the quality of education year after year, the teachers as well as students must engage in R&D activities. Emphasizing R&D may also require a shift on how government grants are disbursed. It will be beneficial to education if a portion of government funds for education is disbursed as grants for furthering R&D through established processes of proposal evaluation and submission of reports at the end. All colleges should be allowed to complete for these funds so there is an incentive even in private institutions to engage in research. In the US, for example, a lot of funding for the universities comes through research grants, which are mostly given by government agencies. Even in private universities, which do not get any direct government funding, a good percentage of their revenue comes from these R&D grants.
Unless R&D is made an integral part of colleges/universities engaged in higher education, education from these places will keep getting further outdated and poorer. To improve the quality of education, the focus should be partly shifted from improving education and syllabi in these places to improving the R&D culture of these places. And to facilitate this, Government has a big role to play in this by not only encouraging the R&D initiatives in these institutions but also by setting mandatory conditions for these institutions to create an R&D infrastructure and support system for students and faculty.
The above efforts will help in rise of GDP apart from nation building…
The Clock is tickling & tickling fast … we have mammoth task ahead to do Political, Economical Social & Strategic reforms implementation. Else we may face voice of Reservation, Separatism, Class Divide, and Social Unrest & Hooliganism in all parts of the country. Wake up call for all of us… let’s tighten our belts & get to work…
- Oct 23, 2017
- Posted by: Deepak Bharara
- Categories: Articles, Knowledge Bank, Wisdom

